Introduction
Bytemask is an Android Gradle Plugin that masks your secret strings for the app in the source code making it difficult to extract from reverse engineering.
How does it work?
1. Plugin - Encrypt strings at the compile time
The plugin is customizable. The default implementation of plugin encrypts strings with the public app signing info (SHA-256) and generated the config class with the encrypted value in the byte array format in the app's source.
2. App - Decrypt strings in the runtime
At runtime, the app retrieves values from the configuration class. These values are decrypted using the SHA-256 hash of the app's signing certificate. This hash is fetched in the runtime using the PackageManager API in Android.
See the flow for better understanding:
How does it generate code?
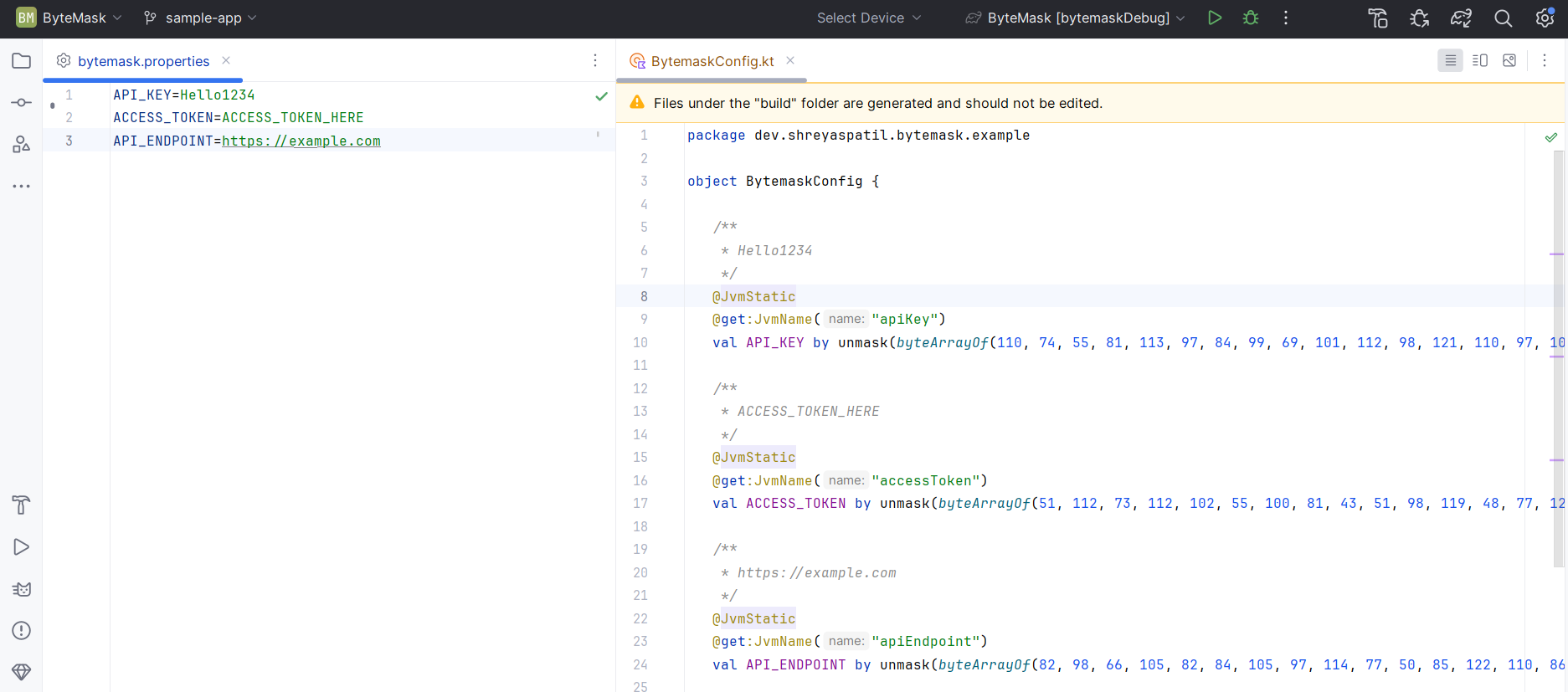
Once you declare the secret properties in .properties file, it generates a class with the properties provided earlier by encrypting them and storing it in the form of bytes.
See image here (Left: Property declarations, Right: Generated class):
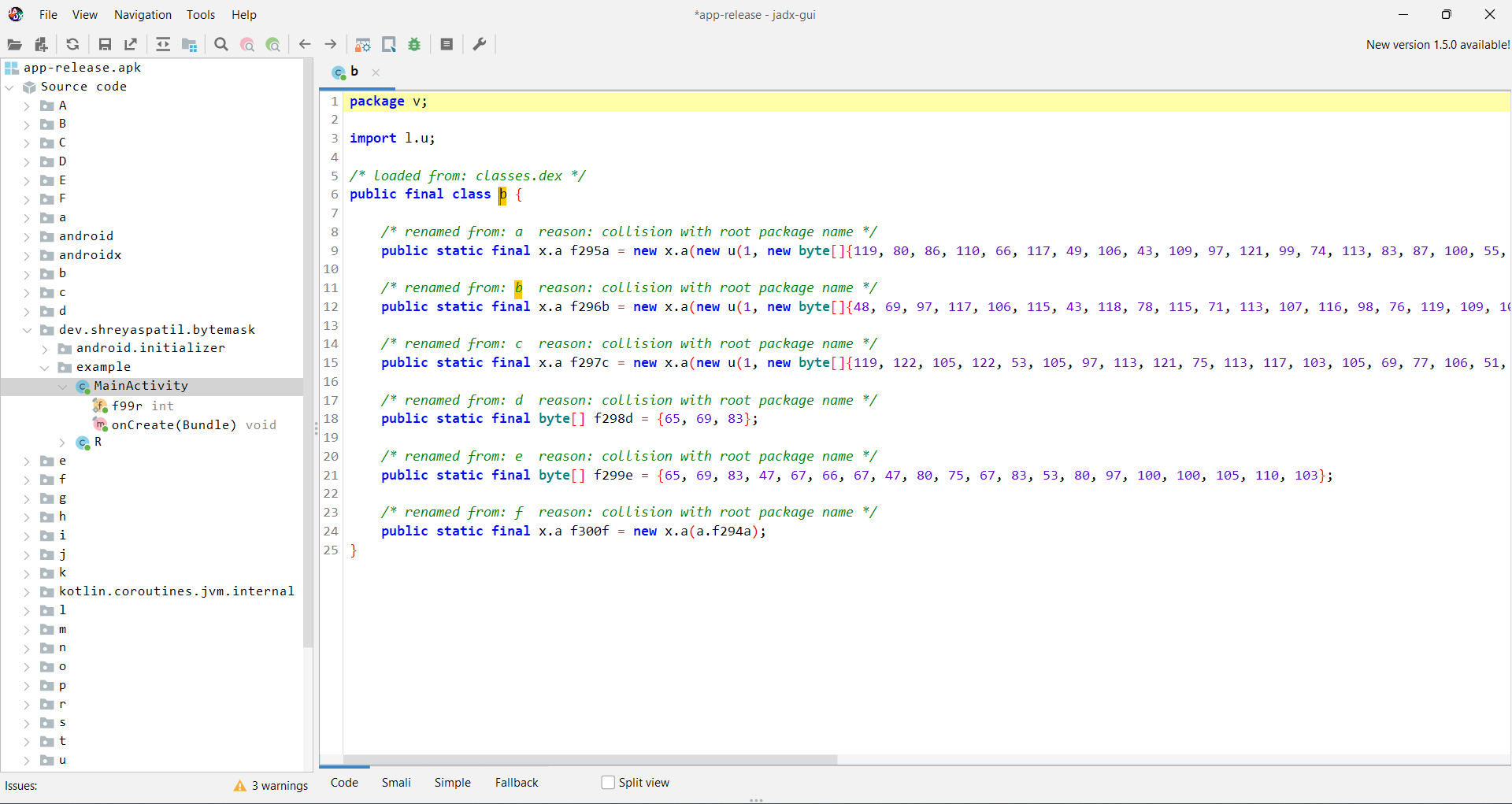
How does it look after reverse engineering on obfuscated APK?
If you build a release APK with R8 obfuscation and optimizations enabled, this is how code looks like which makes it difficult to understand.
See the sample decompiled code (by jadx)
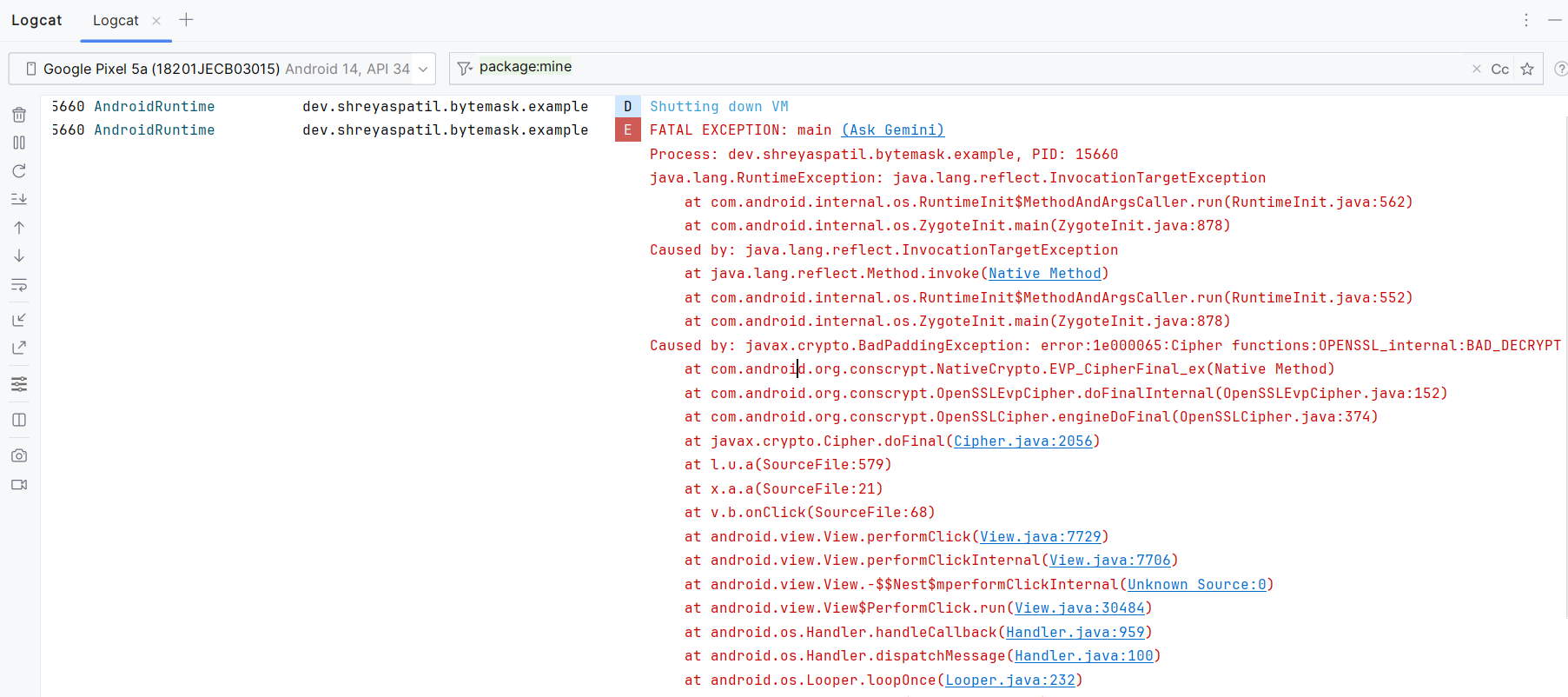
What happens if APK is modified by unauthorized party?
If an unauthorized developer modifies an app (APK) by decompiling and rebuilding it, they won't be able to use the original signing key. This means the modified app will have a different signature.
Since Bytemask encrypted secrets using the app's unique SHA-256 key, any modified app trying to access these secrets will fail (crash) because it won't have the correct key (original SHA-256) in the runtime.
It fails with javax.crypto.BadPaddingException